Controlling
the Equine Estrous Cycle
 96-102 96-102
Why?
- Group mares for breeding with shipped semen
- Preventing estrus during performance races,
shows, and events
- Preventing groups of mares from coming into
estrus when breeding with a single stallion.
- Stop 'horsey' behavior
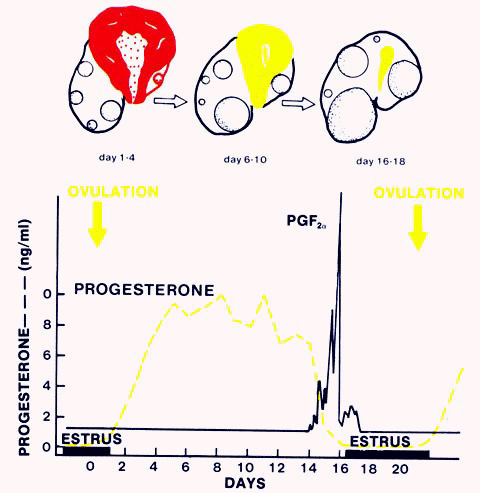
Prostaglandins
- Prostaglandin (PGF) only works on the mature
corpus luteum, which is about 5 days after ovulation.
- The prostaglandin binds receptors on the
mature corpus luteum and causes luteolysis.
- After the administration of prostaglandin to
a mare with a mature corpus luteum the mare will come into heat
2-5 days later.
- The time to estrus varies depending on follicular
development on the ovary.
- If a large follicle is present, the
response is more variable -the mare may ovulate the large follicle
without coming into heat if the follicle is very large and growing
at the time of PGF administration, or if it is large but beginning
atresia when the prostaglandin is given she may regress that
follicle and develop a new wave from which a preovulatory follicle
will arise, in which case it will take her longer to come into
estrus and longer to ovulate.
- Mares with small follicles are
somewhat more predictable in their response to PGF.
- The mare will then ovulate in 7-10 days (ave.).

Products
Lutalyse - Dinoprost
tromethamine
- This is the natural prostaglandin.
- The dose is 5-10 mg (1-2 cc/mare) IM.
- As low as 1.25 to 2.5 mg has
induced a normal estrus in 11 mares with 32 cycles
(Barker. Theriogenology 66 (2006) 686.
- Side effects include transient sweating and
colic.
- Alternatively, a dose of 0.1 to 0.5 mg (0.1
cc) given twice at a 24 hr interval can be used. Side effects
are avoided and efficacy is just as good
Estrumate
- This is a synthetic prostaglandin analogue,
cloprostenol.
- The dose is 200 mcg/mare IM.
- There are fewer side effects to this
prostaglandin product.
Use
- The mare needs a mature corpus luteum, so it
will work in the luteal phase only.
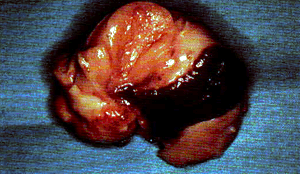
A Mature Corpus Luteum seen on the cut surface of the ovary.
 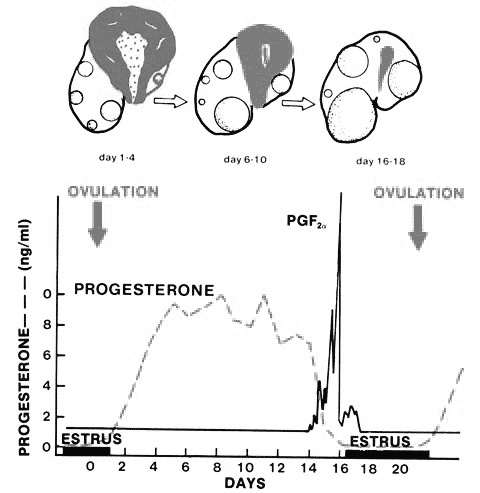
- It will not work to bring anestrus mares into
heat!
- It can be used to "short cycle" a mare,
although the time to ovulation is not as predictable as in cows, nor
is the amount of time "saved"
- It can be
use to terminate a prolonged diestrus
- It will abort a mare in early pregnancy, so
make sure they are not pregnant.
- The induced estrus is normal, and fertility
is no better or worse.
- Administration to a group of cycling mares
allows 'synchronization' of estrous for AI, embryo transfer or
specific breeding arrangements. The true synchrony is not very
good however, because of the variability of the time to estrus,
estrus length and ovulation.
- The drug also allows 'desynchronization', so
if natural cover is used you can keep the mares cycles spread out
so that breeding can be done over a longer time period.
- Careful planning is needed to group mares or
keep mares out of estrus at a particular time
ProgestagensRegumate

- Regumate is an oral progestagen,
allyltrenbolone or altrenogest/
- Administration suppresses estrus by forming
an artificial luteal period.
- The dose is 1 ml/50 kg (1 ml/110 lbs) orally
or in feed for 14 days.
- Heat occurs 4-5 days after withdraw and the
mares have normal fertility.
- The addition of prostaglandin at drug
withdrawal helps the synchrony.
- The drug is fairly expensive, but one of its
benefits is that it has no cross reaction with progesterone
assays, so the endogenous progesterone can be measured while the
drug is being administered.
- The drug can also used in transitional mares
to ease the mare through the transitional period.
- Can also be used at double dose (1 ml/25 kg,
or 2 ml/110 lbs) for 2 days during late estrus in an attempt to
delay ovulation
Injectable progesterone
Estrus suppression
- Progesterone alone does not completely
inhibit follicular development and ovulation
- Injectable progesterone can be used to
suppress estrus, but there is a dose dependent response for
ovulation suppression. For example, 50 mg/day prevents estrus, but
not ovulation; while 100 mg/day prevents estrus and ovulation.
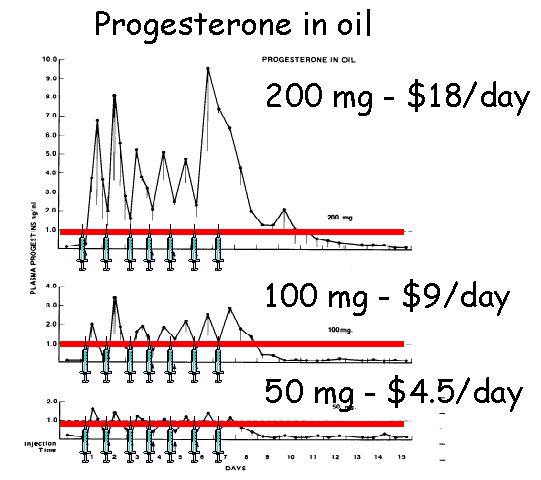
- Administration of 500 mg repositol (alcohol)
every 10 days gives less consistent results for estrus
suppression.
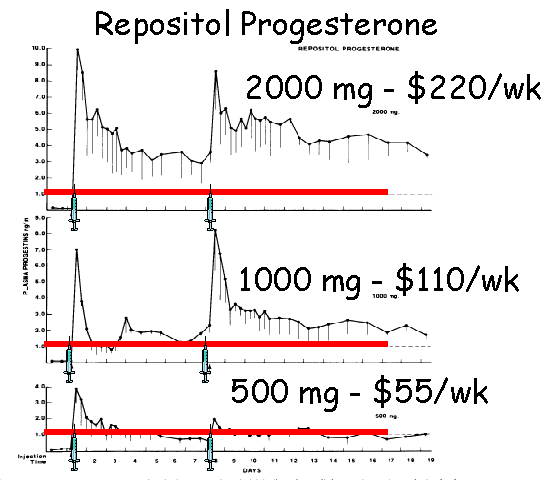
- Commercial products
 BioRelease P4 LA150 BioRelease P4 LA150 - Progesterone 150mg/mL in 'biorelease
technology vehicle'
- $160 for 100 ml
- 10 ml/day (1500 mg) every 7 days for
"pregnancy maintenance"
- ($8/wk)

- Commercial products for estrus
synchronization
- P&E (BET Labs)
- 150 mg progesterone & 10 mg estradiol
- give daily for 10 d
Estrous Synchronization
- Estrogen more profoundly suppresses
follicular development and ovulation than does progesterone
- Intramuscular administration of 150 mg/day
progesterone and 10 mg/day estradiol 17beta
for 10 days, combined with a dose of prostaglandin on the last day
of treatment improves estrous synchronization.
- Addition of 2500 IU hCG when a 35 mm is
present further improves synchronization of ovulation.
- Estradiol 17beta,
however is not commercially at BET labs.
Future Progesterone Products
- P+ Microspheres Progesterone in microspheres
- SABER Progesterone in liquid delivery
system
Alternative
Estrus Suppression Techniques
Temporary

-
Oxytocin
-
60 IU IM BID days 7-14
post ovulation
-
Prolonged CL function
(N=6) to 30-40 days
-
SID seemed as effective
(5/8 vs 5/7 BID vs 1/7 control)
-
Pregnancy
-
Breed and abort
-
Endometrial cups -
prolonged time to estrus
-
Time and expense to breed
-
Stigma of pregnancy and
abortion
-
GnRH vaccine
Permanent
-
Ovaricetomy
- Flank/Midline ovariectomey
- Colpotomy
- Vaginal technique using an ecraseur
- Inexpensive
- Potential complications
- Bleed out
- Remove loop of bowel
- Eviseration
- Laparoscopy - equipment and expertise
Inducing
OvulationhCG

- hCG is a glycoprotein produced by the human
placenta (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) and
found in the urine
of pregnant women.
- The normal dose to induce ovulation is
1,500-3,000 IU IV once during estrus once a 35 mm follicle is
present on the ovary.
- Ovulation normally occurs within about 36-48 hours.
("80% of mares with a follicle > 35 mm will ovulate within 48
hr")
- Work has shown that antibodies will develop
during a breeding season with repeated doses, but the response to
the drug apparently does not diminish.
- Antibodies are carried into the following
year but do not affect the response to hCG
- Some mares fail to respond after use over
several cycles but failure to respond does not correlate with
antibody presence or levels
Ovuplant
Click
to enlarge.
- Ovuplant is a GnRH analog deslorelin
- It was offered as a subcutaneous implant that
was given
when a follicle greater than 30 mm was present on the ovary.
- Deslorelin is now available in injectable
form
- Ovulation will occur within 38-60 hours. Most
people that have used it feel that ovulation occurs about 48 hours
and that it is more consistent than hCG. Published studies
show little difference between hCG and deslorelin in percent of
mares responding, time to ovulation or conception rate.
- Since it is only a decapeptide, antibodies
are not produced.
- It may cause persistent anestrus if
prostaglandin is administered 7 days later, however this in not a
consistent occurrence in all mares.
- With the deslorelin implants, a prolonged
interestrus interval in a fairly high percentage of mares was well
documented. Effects on the interestrus interval with the
injectable deslorelin are not yet clear.
|














 Equine
Index
Equine
Index