Canine
Vaginal Cytology

p 32
Technique
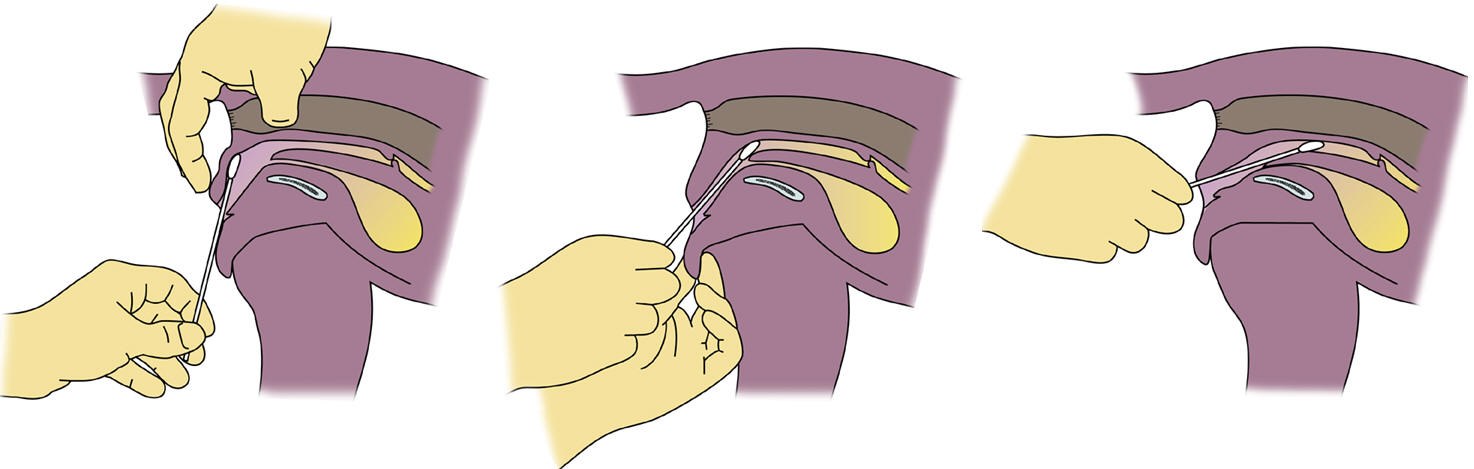
- Moisten a cotton swab with 1 to 2 drops sterile
saline. Open the vulvar lips, pull the vulva doraslly, insert the swab dorsally
and posterior, then up and over
the pelvic brim and into anterior vagina. If you do not pass the swab
far enough, you will get vestibular cells and result in false cornification. If
you pass the swab too ventral, you may enter the bladder and get a
falsely non-cornified smear.
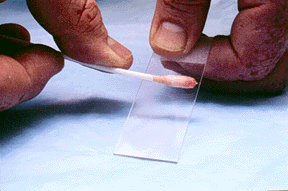
- Roll the swab firmly onto a slide.
- Stain the slide using DifQuik stain, 10 dips in
A, 15 dips in B, and 20 dips in C. You may also use new methylene
blue stain.
- Read the slide under low power first to
establish the trend of cellularity and cell types. Move to a higher
power to establish the cell types. View several fields to get an
overall visual idea of the percentage of cornified cells.
|
|
 |
 |

Click on the movie icon, then right click on the movie or "Open
It" and "OK" to see
a Vaginal Cytology Exam performed |
| Vaginal
Cytology Cell Types |
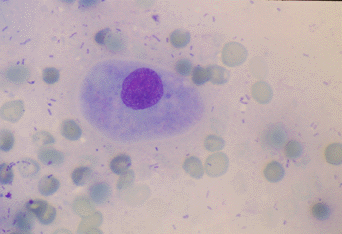
Non-cornified
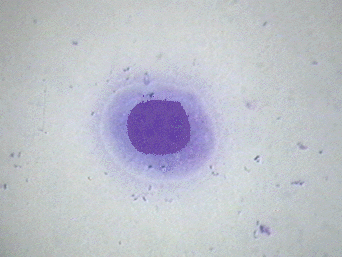
- Parabasal cells have a large stippled nucleus
and a rounded cytoplasm The nucleus is large compared to the
cytoplasm.
- Intermediate cells have a have a stippled
nucleus and more cytoplasm than parabasal cells. The cytoplasm may
even become angular.
|
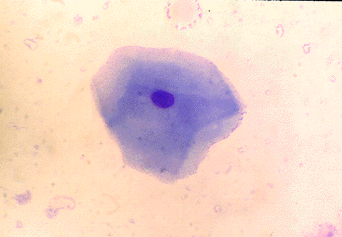
Cornified
Superficial cells have a pyknotic nucleus and
angular cytoplasm. There is no stipling in the nucleus.
Anuclear cells have no visible nucleus and
angular cytoplasm. 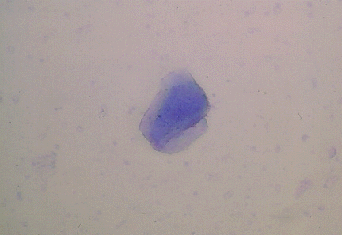
|
Remember
'PISA'
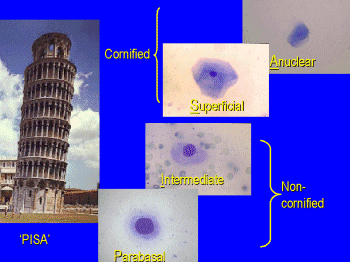
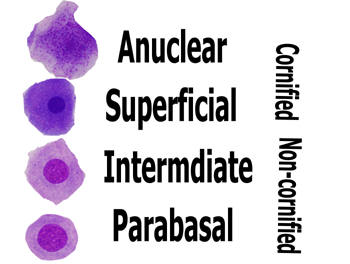
Click picture above to enlarge the
cells.
|
Changes
during the estrous cycle
- When no estrogen is present (anestrus and
diestrus, the vaginal wall is very thin and is comprised of
noncornified cells. In anestrus there will be very few cells and
what you see will be debris and non-cornified cells.
- When estrogen rises during proestrus, the
vaginal epithelium becomes hyperplastic and more cornified. During
proestrus the percent of cornified cells increases by about 10%/day
until you see about 100% cornification during estrus. You may also see
RBCs during proestrus.
|
Thin vaginal epithelium during
anestrus.
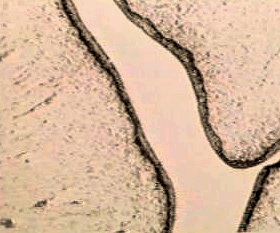 |
Estrus
- During estrus the vaginal epithelium is very
thick. You will see almost 100% cornification. The smear will look
the same from the first day of estrus of the last day of estrus, You
cannot tell which day of estrus the bitch is in based on vaginal
cytology. There may however, be some sheeting of cells during the
last 1-2 days of estrus. The vaginal wall is so thick during estrus
that PMNs do not cross the epithelium. This makes the background
look very 'clean'.
|

|
|
Estrus smear with 100%
cornification and a clear background.
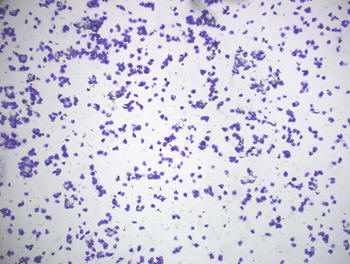
|
Sheets of cells during the end
of estrus. 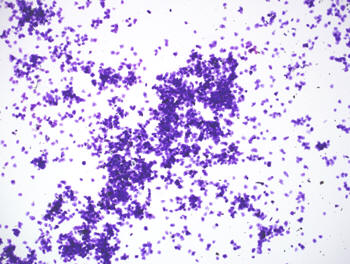
|
Diestrus
- On the first day of diestrus the cells in the
swab abruptly change to around 50% non-cornified. This day that the
smear changes from 100% cornified cells to 50% non-cornified cells
is denoted as the first day of cytologic diestrus. You may see an
influx of PMNs at this time to help clean up all the cellular
debris.
|
Abrupt change
to non-cornified cells on the first day of diestrus.
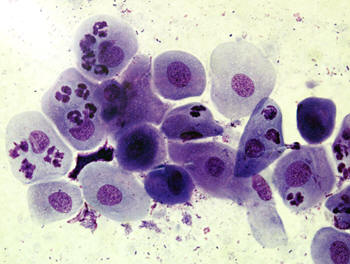
|