|
 |
Meiosis
- Cellular division resulting in the formation of
gametes.
- Consists of two nuclear divisions.
- Results in one gamete each containing 1N
chromosomes,
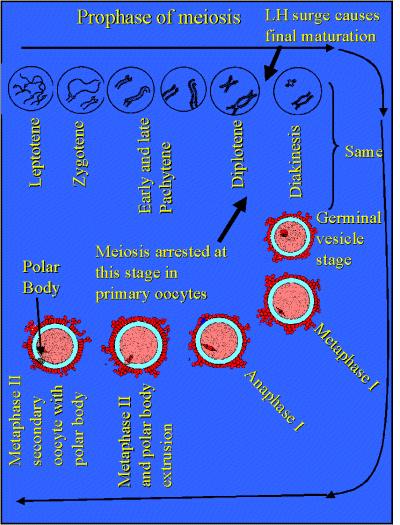
Prophase
- Leptotene - pairing of diploid chromosomes
- Zygotene - transitory pairing stage
- Pachytene - genetic exchange between chromosomes
- Diplotene - resting stage at which oocytes arrest
in primordial follicles.
- Diakinesis or germinal vesicle stage - meiosis
resumes in the Graffian follicle. Caused by the LH from the anterior
pituitary.
Metaphase I
- bivalents arranged on microtubules. Cell divides to
contain 2 1N chromosomes.
- Anaphase - bivalents move to opposite poles. Dog,
fox and horse ovulate this structure.
Metaphase II and polar body extrusion
- a 1N chromosome is expelled (the polar body) to
leave the cell 1 1N chromosome in the secondary oocyte.
- this is the ovulated structure in most species.
|
contributed by Bruce
E Eilts on 22-June-2000
modified by Eric Huey
|
