Canine
Breeding Management
 p553 p553

p 41
- Improper timing of breeding is
often the cause of unsuccessful breeding.
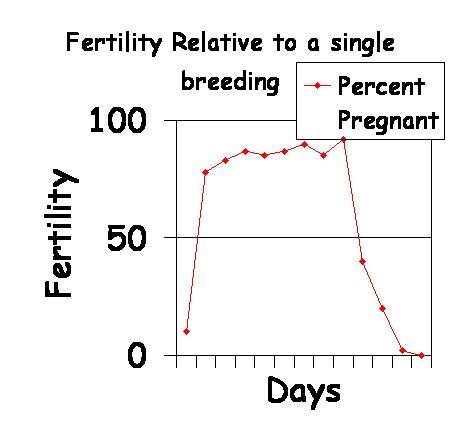
- The conception rate after a
single breeding is highest if the bitch is bred 3-10 days prior to Day 1
of diestrus (D1).
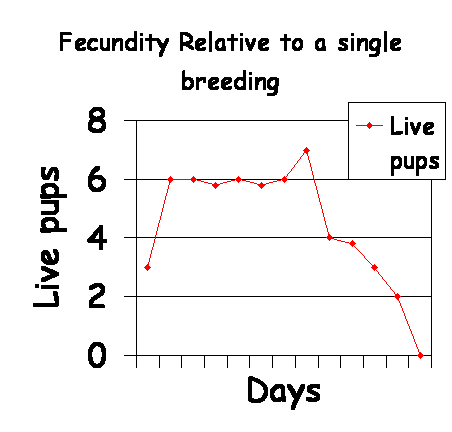
- After a single breeding, the number of live pups per
CL is highest when the breeding occurs 4 days prior to D1 by a proven,
fertile male. This would equate to the fifth day of estrus for an
average, normal 9 day estrus.
Fertile Male
Timing the cycle
for optimal breeding
 553 553  p 49
p 49
-
The estrous cycle should be monitored to
establish when the bitch is actually in estrus.
-
If there are
constraints on the availability of the male, or the number of breedings
possible, it is important that the cycle be monitored carefully to
ensure the optimal time to breed.
-
Management of breedings using shipped,
chilled semen or frozen semen require excellent timing of the fertile
period.
-
Methods for timing a breeding include:
-
Behavior of the
bitch, such as flagging the tail and standing to be mounted.
-
Physical
signs such as:
-
Vulvar swelling
-
Bloody discharge.
-
Vaginal cytology
-
Ultrasound examination of ovarian follicular
activity
-
Hormone assay
for either progesterone or LH.
-
While vaginal cytology is fairly
reliable, all other methods are unreliable except for hormone assay.
-
Hormone assays are the best way to determine the fertile period.
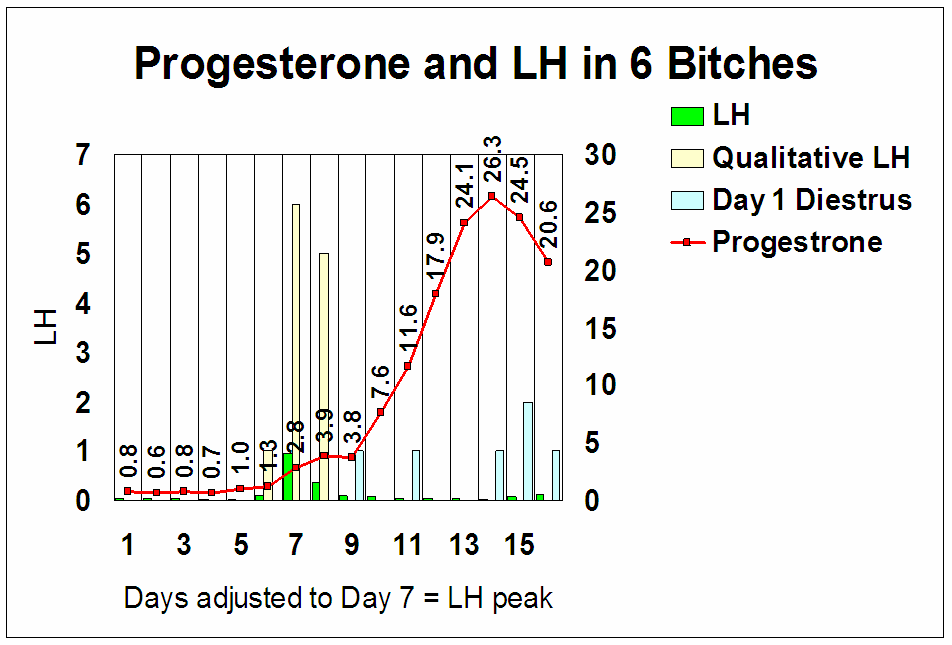
Relative progesterone concentrations during the
proestrual/estrual period.
P4 (ng/ml)
Relative time points
1.1-1.9 Before LH surge
2.1-2.9 Day of LH surge
3.1-3.9 Days 1-2 after the LH surge
4.0-8.0 Day of ovulation
10-80 2-3 weeks post-ovulation
Progesterone
concentrations and day of cycle
relative to LH peak (from LSU
data)
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
P4 ng |
Day |
|
1.0 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.3 |
3 |
|
11.7 |
4 |
|
17.1 |
5 |
|
22.5 |
6 |
|
27.9 |
7 |
|
1.1 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.4 |
3 |
|
11.8 |
4 |
|
17.2 |
5 |
|
22.6 |
6 |
|
28.0 |
7 |
|
1.2 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.5 |
3 |
|
11.9 |
4 |
|
17.3 |
5 |
|
22.7 |
6 |
|
28.1 |
7 |
|
1.3 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.6 |
3 |
|
12.0 |
4 |
|
17.4 |
5 |
|
22.8 |
6 |
|
28.2 |
7 |
|
1.4 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.7 |
3 |
|
12.1 |
4 |
|
17.5 |
5 |
|
22.9 |
6 |
|
28.3 |
7 |
|
1.5 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.8 |
3 |
|
12.2 |
4 |
|
17.6 |
5 |
|
23.0 |
6 |
|
28.4 |
7 |
|
1.6 |
Pre-LH |
|
6.9 |
3 |
|
12.3 |
4 |
|
17.7 |
5 |
|
23.1 |
6 |
|
28.5 |
7 |
|
1.7 |
Pre-LH |
|
7.0 |
3 |
|
12.4 |
4 |
|
17.8 |
5 |
|
23.2 |
6 |
|
28.6 |
7 |
|
1.8 |
Pre-LH |
|
7.1 |
3 |
|
12.5 |
4 |
|
17.9 |
5 |
|
23.3 |
6 |
|
28.7 |
7 |
|
1.9 |
Pre-LH |
|
7.2 |
3 |
|
12.6 |
4 |
|
18.0 |
5 |
|
23.4 |
6 |
|
28.8 |
7 |
|
2.0 |
0 |
|
7.3 |
3 |
|
12.7 |
4 |
|
18.1 |
5 |
|
23.5 |
6 |
|
28.9 |
7 |
|
2.1 |
0 |
|
7.4 |
3 |
|
12.8 |
4 |
|
18.2 |
5 |
|
23.6 |
6 |
|
29.0 |
8 |
|
2.2 |
0 |
|
7.5 |
3 |
|
12.9 |
4 |
|
18.3 |
5 |
|
23.7 |
6 |
|
29.1 |
8 |
|
2.3 |
0 |
|
7.6 |
3 |
|
13.0 |
4 |
|
18.4 |
5 |
|
23.8 |
6 |
|
29.2 |
8 |
|
2.4 |
0 |
|
7.7 |
3 |
|
13.1 |
4 |
|
18.5 |
5 |
|
23.9 |
6 |
|
29.3 |
8 |
|
2.5 |
0 |
|
7.8 |
3 |
|
13.2 |
4 |
|
18.6 |
5 |
|
24.0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
2.6 |
1 |
|
7.9 |
3 |
|
13.3 |
4 |
|
18.7 |
5 |
|
24.1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
2.7 |
1 |
|
8.0 |
3 |
|
13.4 |
4 |
|
18.8 |
5 |
|
24.2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
2.8 |
1 |
|
8.1 |
3 |
|
13.5 |
4 |
|
18.9 |
5 |
|
24.3 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
2.9 |
1 |
|
8.2 |
3 |
|
13.6 |
4 |
|
19.0 |
5 |
|
24.4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.0 |
1 |
|
8.3 |
3 |
|
13.7 |
4 |
|
19.1 |
5 |
|
24.5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
1 |
|
8.4 |
3 |
|
13.8 |
4 |
|
19.2 |
5 |
|
24.6 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
1 |
|
8.5 |
3 |
|
13.9 |
4 |
|
19.3 |
5 |
|
24.7 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
1 |
|
8.6 |
3 |
|
14.0 |
4 |
|
19.4 |
5 |
|
24.8 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.4 |
1 |
|
8.7 |
3 |
|
14.1 |
4 |
|
19.5 |
5 |
|
24.9 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
1 |
|
8.8 |
3 |
|
14.2 |
4 |
|
19.6 |
5 |
|
25.0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.6 |
2 |
|
8.9 |
3 |
|
14.3 |
4 |
|
19.7 |
5 |
|
25.1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.7 |
2 |
|
9.0 |
3 |
|
14.4 |
4 |
|
19.8 |
5 |
|
25.2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.8 |
2 |
|
9.1 |
3 |
|
14.5 |
4 |
|
19.9 |
5 |
|
25.3 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
3.9 |
2 |
|
9.2 |
3 |
|
14.6 |
4 |
|
20.0 |
5 |
|
25.4 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.0 |
2 |
|
9.3 |
3 |
|
14.7 |
5 |
|
20.1 |
5 |
|
25.5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
2 |
|
9.4 |
3 |
|
14.8 |
5 |
|
20.2 |
5 |
|
25.6 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
2 |
|
9.5 |
3 |
|
14.9 |
5 |
|
20.3 |
5 |
|
25.7 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
2 |
|
9.6 |
3 |
|
15.0 |
5 |
|
20.4 |
5 |
|
25.8 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
2 |
|
9.7 |
3 |
|
15.1 |
5 |
|
20.5 |
5 |
|
25.9 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
2 |
|
9.8 |
3 |
|
15.2 |
5 |
|
20.6 |
5 |
|
26.0 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
2 |
|
9.9 |
3 |
|
15.3 |
5 |
|
20.7 |
5 |
|
26.1 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.7 |
2 |
|
10.0 |
3 |
|
15.4 |
5 |
|
20.8 |
5 |
|
26.2 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
4.8 |
2 |
|
10.1 |
4 |
|
15.5 |
5 |
|
20.9 |
5 |
|
26.3 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
4.9 |
2 |
|
10.2 |
4 |
|
15.6 |
5 |
|
21.0 |
6 |
|
26.4 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.0 |
3 |
|
10.3 |
4 |
|
15.7 |
5 |
|
21.1 |
6 |
|
26.5 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.1 |
3 |
|
10.4 |
4 |
|
15.8 |
5 |
|
21.2 |
6 |
|
26.6 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.2 |
3 |
|
10.5 |
4 |
|
15.9 |
5 |
|
21.3 |
6 |
|
26.7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.3 |
3 |
|
10.6 |
4 |
|
16.0 |
5 |
|
21.4 |
6 |
|
26.8 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.4 |
3 |
|
10.7 |
4 |
|
16.1 |
5 |
|
21.5 |
6 |
|
26.9 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.5 |
3 |
|
10.8 |
4 |
|
16.2 |
5 |
|
21.6 |
6 |
|
27.0 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.6 |
3 |
|
10.9 |
4 |
|
16.3 |
5 |
|
21.7 |
6 |
|
27.1 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.7 |
3 |
|
11.0 |
4 |
|
16.4 |
5 |
|
21.8 |
6 |
|
27.2 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.8 |
3 |
|
11.1 |
4 |
|
16.5 |
5 |
|
21.9 |
6 |
|
27.3 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
5.9 |
3 |
|
11.2 |
4 |
|
16.6 |
5 |
|
22.0 |
6 |
|
27.4 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
6.0 |
3 |
|
11.3 |
4 |
|
16.7 |
5 |
|
22.1 |
6 |
|
27.5 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
6.1 |
3 |
|
11.4 |
4 |
|
16.8 |
5 |
|
22.2 |
6 |
|
27.6 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
6.2 |
3 |
|
11.5 |
4 |
|
16.9 |
5 |
|
22.3 |
6 |
|
27.7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.6 |
4 |
|
17.0 |
5 |
|
22.4 |
6 |
|
27.8 |
7 |
|
|
|
Click either graph to enlarge
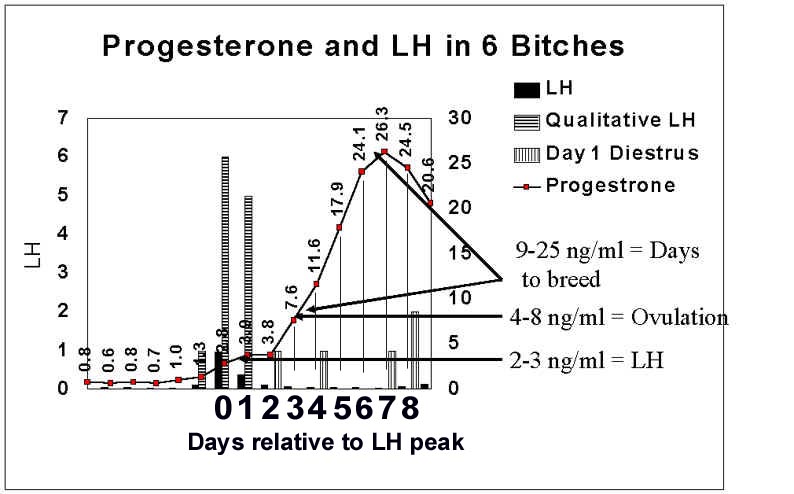
Progesterone
testing (see Appendix C)
Qualitative
Hormone Analysis
-
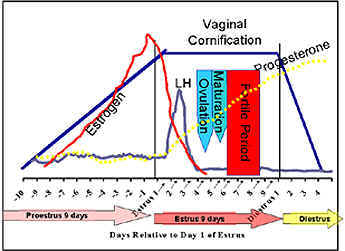
The initial progesterone rise during estrus in
the bitch coincides with the LH peak.
-
Before the LH peak the
progesterone is < 1.0 ng/ml.
-
On the day of the LH peak, progesterone
rises to around 1.5 - 2.0 ng/ml. Thereafter the progesterone is > 5
ng/ml.
-
Using our lab ovulation
occurs at about 3.8-5.0 ng/ml (11.7 nmol/L) of progesterone
(including the day of ovulation and the 24 hours it takes to
ovulate) and the best days to breed occur at about 17.6-24.1 ng/ml
(54-74 nmol/L) of progesterone.
-
The progesterone can be assayed quantitatively by a laboratory or
qualitatively using an ELISA kit.
-
The ELISA kits are quick and
semi-quantitative.
-
Use the ELISA kits as an adjunct to vaginal cytology.
-
Begin when vaginal cornification reaches 60 - 75%.
-
If used alone, begin
third or fourth day of proestrus. Test every other day.
-
The
'Status-Pro' will
indicate the day of if initial progesterone rise by the number of blue
dots fading.
-
The 'Target'
test is read
by the
intensity of
the dot
color.
Target
test
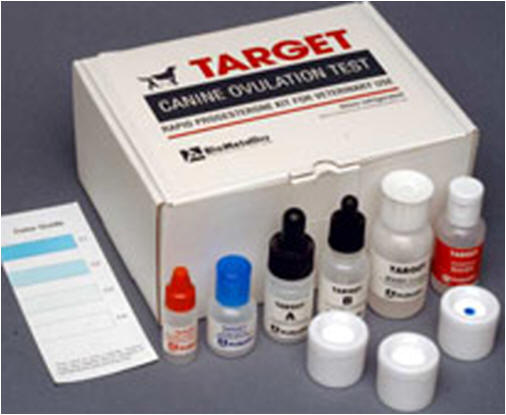
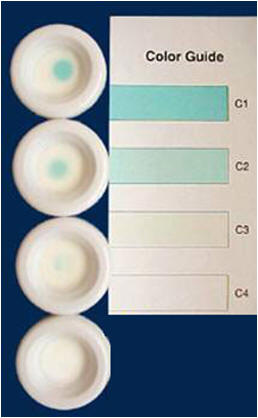 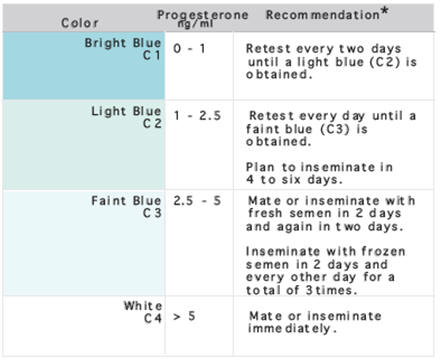
Status Pro

Premate
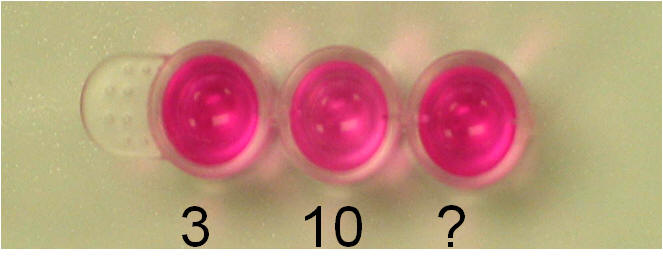
-
'Ovucheck
Premate'
has you read
wells and
compare the
sample to a
set of
controls for
color
intensity.
-
It has ranges of < 3, 3-10 and >
10.
-
These ranges do not fit well
with breeding protocols we use.
-
Handy to determine early vs late
estrus.
K9
Proges-Check
-
It is important to do follow-up testing to
ensure that progesterone continues to rise, as sometimes the dogs become
'stuck' at 2-7 ng/ml. This may indicate an anovulatory cycle.
-
It is also
important to continue to follow the vaginal cytology.
-
Counting back 6
days from the first day of cytologic diestrus should coincide with
ovulation. (This would be 8 days from the LH peak).
-
If these two tests
do not predict ovulation on a similar day, then fertility may be
compromised.
-
If you skipped a day between tests and the test today is
high and the test 2 days ago was low, then
the day in between was the day of initial progesterone rise.
USING PROGESTERONE KITS TO
TIME INSEMINATION IN THE BITCH

Dale Paccamonti, D.V.M., M.S., Dip.
A.C.T.
When the number of breedings is reduced to one or
two during a single estrus, such as with frozen or fresh cooled semen,
timing insemination to coincide with ovulation becomes critical.
Ovulation occurs approximately two days after the LH surge. The bitch
ovulates primary oocytes which require two to three more days for
maturation. Mature oocytes are then viable for another two to three
days. Therefore, the fertile period is four to eight days after the LH
surge with peak fertility occurring five to six days after the LH surge.
Vaginal cytology does not give a very precise
prediction of ovulation. The LH peak may occur anywhere from the same
day, or up to two days after, full cornification. Unlike most species,
progesterone rises before ovulation in the bitch. Therefore,
progesterone is useful to predict the LH surge as an increase in serum
progesterone is closely associated with the LH peak. Before the LH
surge, progesterone is < 1 ng/ml. On the day of the LH surge,
progesterone rises to 1.5 to 2.0 ng/ml and thereafter continues to rise
during diestrus or pregnancy. By identifying this initial rise in
progesterone, the day of the LH surge can be estimated and insemination
performed during the period of peak fertility .
At least two kits are available for in-house,
semi-quantitative progesterone testing. Both are CITE kits and are
interpreted on the basis of color changes. The Target Kit (Biometallics,
Inc., Princeton, NJ; 800-999-1961) differentiates between different
concentrations of progesterone on the basis of the color intensity of a
single dot. A bright blue dot corresponds to a progesterone
concentration of 0.0 to 1.0 ng/ml, light blue: 1.0 to 2.5 ng/ml, very
pale blue: 2.5 to 5.0 ng/ml, and white: greater than 5.0 ng/ml. The
Target kit includes an internal calibration which eliminates the need to
run a control or to have multiple spots in the test. The Status Pro
(International Canine Genetics, Malvern, PA, 19355; 800-248-8099) uses
three dots to differentiate between 0.0 to 1.5 ng/ml (3 dots), 2.0 to
7.0 ng/ml (2 dots) and greater than 7.5 ng/ml (1 dot) serum
progesterone. The dot which is visible at high progesterone
concentrations serves as a control.
Progesterone testing can be used as an adjunct to
vaginal cytology or can be used alone if a practitioner is not
comfortable interpreting vaginal cytology. If progesterone testing is to
be used in conjunction with vaginal cytology, testing should begin when
vaginal cytology is approximately 60-75% cornified to establish a
baseline with which to compare subsequent test results. If using
progesterone tests alone, test every other day, beginning early (3rd or
4th day) in proestrus.
Using the Status Pro kit, the low spot will begin
to fade on Day 0 (the day of the LH peak) and will disappear on Day 1
post LH peak. The serum progesterone on Day 1 may occasionally vary and
the dot may not completely disappear. In these cases, though, rising
progesterone can be detected by fading of the low progesterone dot.
Using the Target kit, fading of the dot or the presence of a light blue
dot corresponds to the initial rise in progesterone, or day 0, the day
of the LH peak.
Both tests come with concise, step-by-step
instructions. The tests are easy to perform and results are available in
about 20 minutes. Some aspects of the tests require attention to detail
to achieve meaningful results. The kits need to come to room temperature
before use. If the test is run using a cold kit, results will be
incorrect, often giving a false high progesterone. The manufacturers
recommend the kits be placed at room temperature for approximately two
hours before use. Blood should be collected into a plain (red top) tube
without anticoagulant for the Status Pro. For the Target kit, blood
should be collected in either a plain (red top), EDTA (purple) or
heparin (green) coated tube. Blood should be allowed to clot at a cool
temperature (in the refrigerator) and cells should be separated from
serum or plasma as soon as possible (within 20 minutes of collection is
the manufacturer's recommendation). If serum is allowed to remain with
the red blood cells, progesterone will be bound by them and test results
will be artificially low. With the Target kits, hemolyzed or lipemic
samples may be used but additional washes (Step 2) should be performed
before adding the enzyme (Step 3). Hemolyzed or lipemic samples will
give a false low progesterone if used with the Status-Pro kits. Serum
samples may also be frozen for analysis at a later date.
If insemination is to be performed with fresh
semen and multiple breedings are possible, insemination may be performed
every other day after the initial rise in progesterone is observed. If
only two breedings are to be performed, insemination should be performed
on either Days 3 and 5 or Days 4 and 6. Likewise, if insemination
involves fresh chilled semen, fertility is best if breedings occur on
Days 3 and 5 or 4 and 6, keeping in mind that viability of fresh chilled
semen is reduced and timing of insemination is more critical. The
viability of frozen semen is reduced even further and timing is even
more critical. If multiple vaginal inseminations with cryopreserved
semen are to be performed, they should be performed on Days 4, 5 and 6.
More commonly, a single surgical insemination is conducted when frozen
semen is used. Surgical insemination with frozen semen should be
performed on Day 5 or 6.
After the day of the LH surge is determined and
insemination has been performed, vaginal cytology samples should be
collected every other day until Day 1 of diestrus is determined. This
provides another means, although retrospective, to determine the day of
ovulation. Determining the day of ovulation by two methods and
determining if they coincide may help in an infertility workup.
Semi-quantitative progesterone kits may also be used three to four weeks
after the end of estrus to verify that progesterone is high when luteal
insufficiency or ovulation failure are suspected.
Quantitative Progesterone
Some
laboratories offer a 24 hour turn around on quantitative serum
progesterone.
-
LSU SVM
Theriogenology


-
Same day if
notified by 12:00 and sample here by 3
-
Saturday testing
available if notified on Friday
-
Current cost
- ~ $40, $70 for
Stat samples (Saturday)
-
Dr. Robert Hutchinson also states that the LH surges
occurs when the quantitative progesterone is 2-3 ng/ml. However, Dr. Pat
Concannon believes that it is the rate of the progesterone rise from the
preceding days that indicates the LH surge, not the value or magnitude.
For example, it may increase from 0 .4 to 0 .8 ng/ml, 0.7 to 1.2 ng/ml,
or 0.8 to 2.0 ng/ml. Other people state that the dog ovulates when
quantitative progesterone reaches 5.0 ng/ml. We have not been able to
correlate quantitative progesterone that we have run to known ovulation
dates, whereas some people rely heavily upon it.
LH
testing - Status LH or Witness


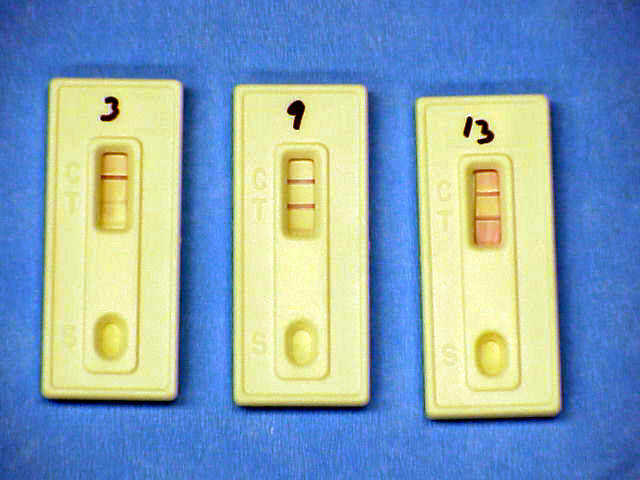
The
Witness LH test is also a quick qualitative ELISA test. It must
be run daily, because the LH has only a one day rise, and if a day of LH
testing is missed the LH peak may have been missed. This test is
reliable, but since testing must be done daily, it is usually more time
consuming and expensive. If a single day is missed, the LH peak may have
been missed. Experimentally, this has been very accurate at determining
the LH peak for us.
Click to enlarge


Breeding
Artificial
Insemination of Fresh Semen
 p 57 p 57
-
It is always best to use proven male, but always evaluate
the semen to determine the number of cells and the quality of the cells
inseminated.
-
Breed every other day during estrus until the first day of
cytologic diestrus.
-
Insert a pipette over the pubis and into the
anterior vagina. Be careful to avoid urethra and inseminate the bladder,
as pregnancy rates are low with insemination into the
bladder.
-
A cow AI
sheath or a cut-off cow infusion pipette works well for most bitches.
-
Some smaller dogs may require a smaller pipette.
-
Commercial pipettes are
available specifically for dogs.
-
Generally, an unskilled person working
with regular equipment cannot enter the bitch's cervix. The cervix is
difficult to enter because it is actually at a 90 degree angle
to the animals longitudinal axis.
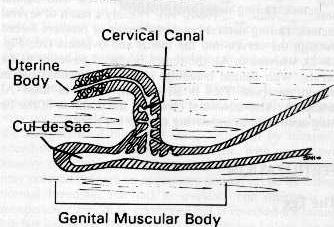
- Infuse
the unextended semen.
- A regular syringe can be used because the sperm
cells are not in contact with the syringe very long.
- Some syringes have
been implicate as being spermacidal.
- It has been traditional to
feather the dorsal vagina and to elevate the hindquarters for 10
minutes, but our research has shown neither of these to be
necessary.
- As always,
remember to do your AKC paperwork.
- How many cells are needed?
- Vaginal AI on 3 consecutive days after
acceptance of the male by the female with 50 X 106 cells
of fresh semen extended 1:4 resulted in lower fertility (20%)
than AI on 3 consecutive days with 200 x 106
cells of fresh semen extended 1:1 (80%) or natural mating (80
%).
- The volume fresh semen placed in the anterior
vagina has not been critically evaluated.
- Volumes as low as 2.2 ml and up to
3.6-3.9 ml have been reported to yield good pregnancy
rates.
- As long as an adequate number of cells is
placed into the vagina, the volume of the inseminate does not
affect fertility.
- Excessively large semen volumes inseminated
into the vagina could result in the drainage of some of the
ejaculate from the vagina, however this has not been critically
tested.
- There is only one controlled study that
directly compared pregnancy rates of bitches bred by AI using
fresh semen vs. natural mating, and it showed there was no
difference in pregnancy rates of bitches mated by AI or natural
mating when the same males were used under similar breeding
conditions.
- Transcervical insemination (see below under Frozen
Semen for more information)
- Fertility after intrauterine insemination of
fresh semen was greater than that obtained by vaginal AI with
fresh semen, but the vaginal AI conception rate was only 25% in
one report.
- Intrauterine insemination with fresh semen
appears to have no benefits under most normal situations
- One report indicates intrauterine insemination
with fresh semen significantly improved the pregnancy rates in
bitches that were previously infertile when bred to the males
that proved fertile in breeding other bitches.
- At LSU (EVSSAR 2005 Budapest)
-
A
total
of
11
females
during
82
estrous
cycles
(59
AI
and
23
TCI)
were
evaluated.
- Eleven different males were used for 1 to 22 estrous cycles (mean = 7, SD = 6.2). There was no difference among female or male fertility.
- The median number of TCIs performed for each female (+ SD) in the TCI group was 2 + 0.99.
- The pregnancy rates for bitches in the AI and TCI groups were 38.3% (33/59) and 83.3% (20/23), respectively. The odds ratio of a female becoming pregnant in the TCI group was 10.8 (p = 0.005).
- The average number of total breedings (+ SD) in the TCI and AI groups was not different (4.3 + 1.1 and 3.9 + 1.4, respectively).
- The average number of total cells inseminated (+ SD) in the TCI and AI groups was not different (1802 + 1085 and 1226 + 1121, respectively).

Click to see a video of artificial insemination in the bitch.
Breeding when only 1 or 2 breedings are
available
(Limited availability of stud, shipped or frozen semen)
-
If fresh cooled shipped semen is being sent in, it is
important to predict the fertile period.
-
The "Fertile period"
is 4 to 8 days after the LH surge.
-
This is because the ovulation occurs
2 days after the LH surge and takes around 24 hours
- Then the oocyte
must undergo reduction division, which takes another 24 hours
- ....hence
at least 4 days past the LH surge.
- The oocytes are viable for only a
short though after the reduction division, so the peak fertility is 5 to
6 days after the LH peak.
- It is recommended to breed on days 3 and 5 or
days 4 and 6 after the LH peak.
- The insemination procedure is the same as
with fresh semen. There is no need to warm the semen before
insemination, but a sample should be analyzed to ensure quality.
- Results
after using chilled extended semen can be the same as natural
breeding if the proper number of cells are inseminated enough times.
- Swedish
reports that summarized data from chilled semen inseminations show
pregnancy rates can vary from 28-60% depending upon the type of
extender used.
- These
pregnancy rates are lower when ovulation is timed and the number
of breeding is limited than when compared to the 90-100%
conception rates when an average of 4 breedings of 250-350 x 106
cells/breeding were used by us.
 Packaging cooled
semen Packaging cooled
semen
 p 59 p 59
-
After semen collection, analyze the sample and extend at
least 1:1 in warm extender.
-
We have found that the skim milk equine
extender works as well as most of the commercial or home-made canine
extenders.
-
Package in a cooling system. Again, we have found the equine
packaging systems work as well as the more expensive commercial
canine packaging systems.
-
At this time the AKC requires all studs that have semen
chilled and shipped to be DNA tested before registration of pups is
allowed.
 Click
here to link to the AKC page on DNA testing and AI. Click
here to link to the AKC page on DNA testing and AI.

Click on the AKC logo
to go to the AKC Homepage
 Click
here to link to the AKC page on AI Regulations. Click
here to link to the AKC page on AI Regulations.
 Frozen semen Frozen semen
 p 60 p 60
-
If frozen semen is being used, surgical insemination
generally gives the highest fertility.
-
Since the frozen cells do not
live as long, breed on day 5 or 6 after the LH peak.
-
A ventral midline
laparotomy is performed, the uterine horns exposed with minimal trauma,
and the thawed semen is injected into either horn.
-
Thaw the semen only
when you are ready to inseminate and use the thawing directions supplied
by the freezing company, no matter how you normally do it!
-
Check the
motility of a drop before insemination.
-
Use only semen from AKC approved
centers, or the puppies will not be able to be registered with the AKC.
-
AKC paperwork is essential.
-
Vaginal insemination with frozen semen generally has poor
conception, because most people cannot penetrate the cervix.
-
With
special training, however, some people have been able to obtain
acceptable pregnancy rates if breedings occurred on days 4, 5, and 6 after
the LH peak.
-
A 1996 report in Veterinary Record
by Silva, Onclin, Lejune and Verstegen state a 60 % conception rate
using vaginal AI of 1 billion cells with 60% motility on days 3 and 5
after the LH peak.
-
This was the same pregnancy rate using 400 million
cells surgically inseminated.
-
A group of controls using fresh semen had
100 % conception rates.
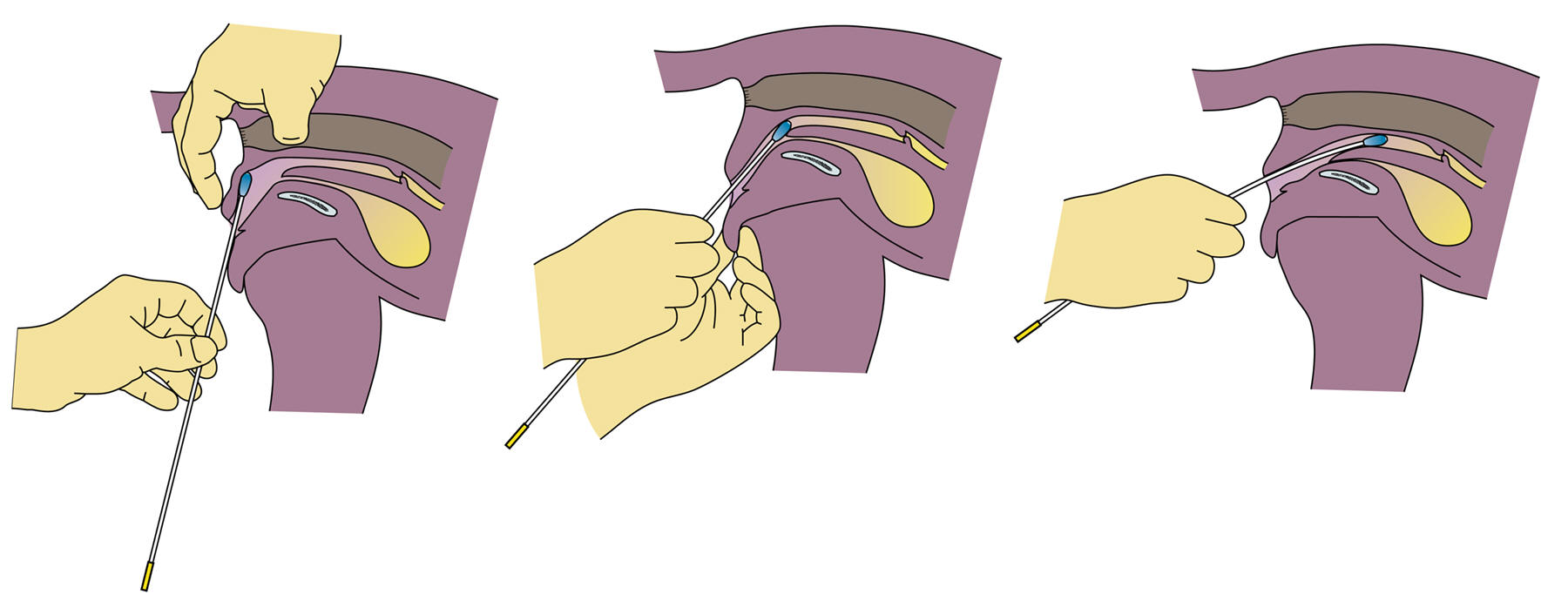
- Norwegian Catheter
- The
catheter consists of a large plastic sheath and a smaller
stainless steel catheter that fits inside the sheath.
- There
are at least three sizes of catheters made for different size
dogs.
- To
perform the insemination
- The
sheath, with the internal catheter in place, is passed as
far into the vagina as possible.
- The
tip of the stainless steel catheter is then advanced
cranially into the fornix under the cervix.
- Since
the cervical os opens in a dorso-ventral direction, the
catheter cannot be directly advanced through the
cervix.
- The
cervix must be palpated through the abdomen and grasped by
the veterinarian.
- Once
the cervix is grasped and the catheter is in the cervical
fornix, the cervix is manipulated by turning in ventrally so
the cervical os assumes a more horizontal position.
- As
the cervix assumes a horizontal orientation, the catheter is
backed out of the fornix and threaded through the cervix
- When the catheter encounters the cervix, a
‘gritty’ sensation is felt by the veterinarian.
- Once the catheter is placed through the
cervix, the semen is inseminated.
- The purchase of the catheters is a relatively
small expense; however attaining the skill to consistently pass
the catheter through the cervix requires considerable training,
practice and patience.
- The possibility of a vaginal or uterine rupture
is always present when inexperienced clinicians are attempting
this intrauterine insemination procedure.
- Conception Rates
- Intrauterine
deposition of frozen semen yielded pregnancy rates of 67%
breeding 1-2 times (the number of cells was not
stated),
- 83%
breeding two times using 200 x 106 cells/breeding
- 84%
breeding 1-3 times using 186 x 106
cells/breeding.
- Increasing the number of breedings from 1
to 3 did not significantly increase the conception rate
using the Norwegian transcervical technique.
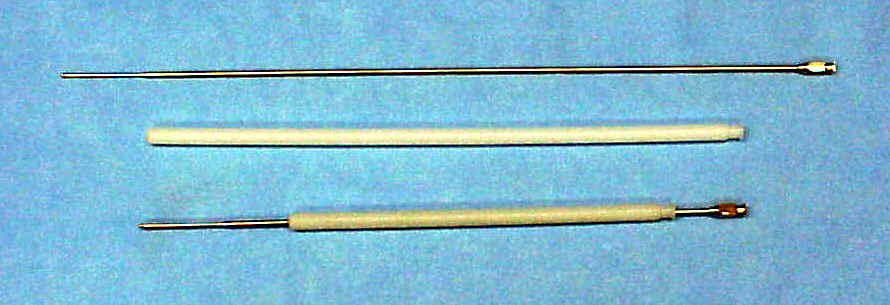
The 'Norwegian' Catheter above
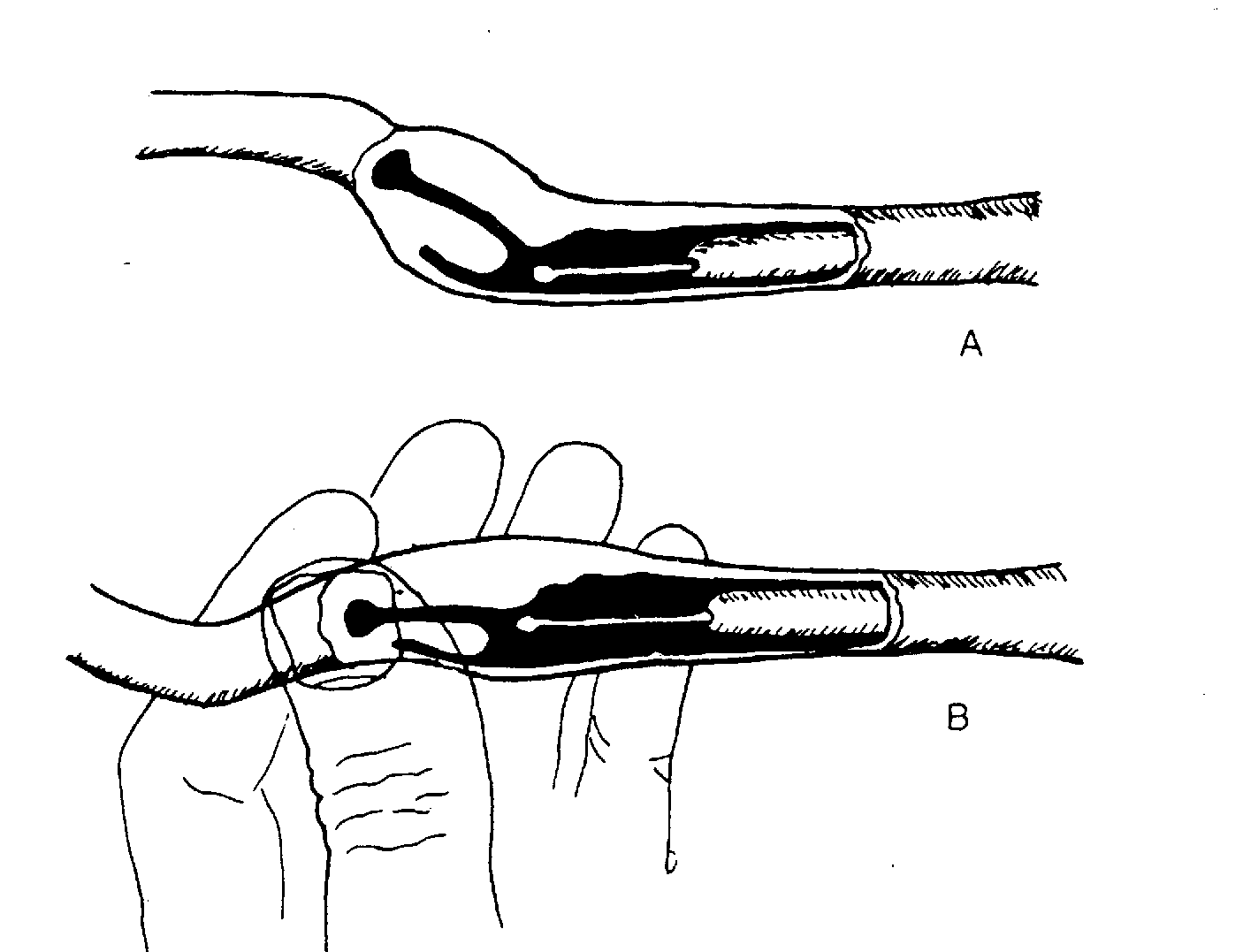
-
A transcervical AI technique has been described by
Marion Wilson from New Zealand.

Click here to see
a
video
by Marion
Wilson of a TCI (edited by Eilts)
- A 36 cm Storz cystoscope with a 300 vewing
angle is used.
- A 55 cm scope with a 60 viewing angle is also used (smaller diameter) if the vagina is smaller, or more length is needed.
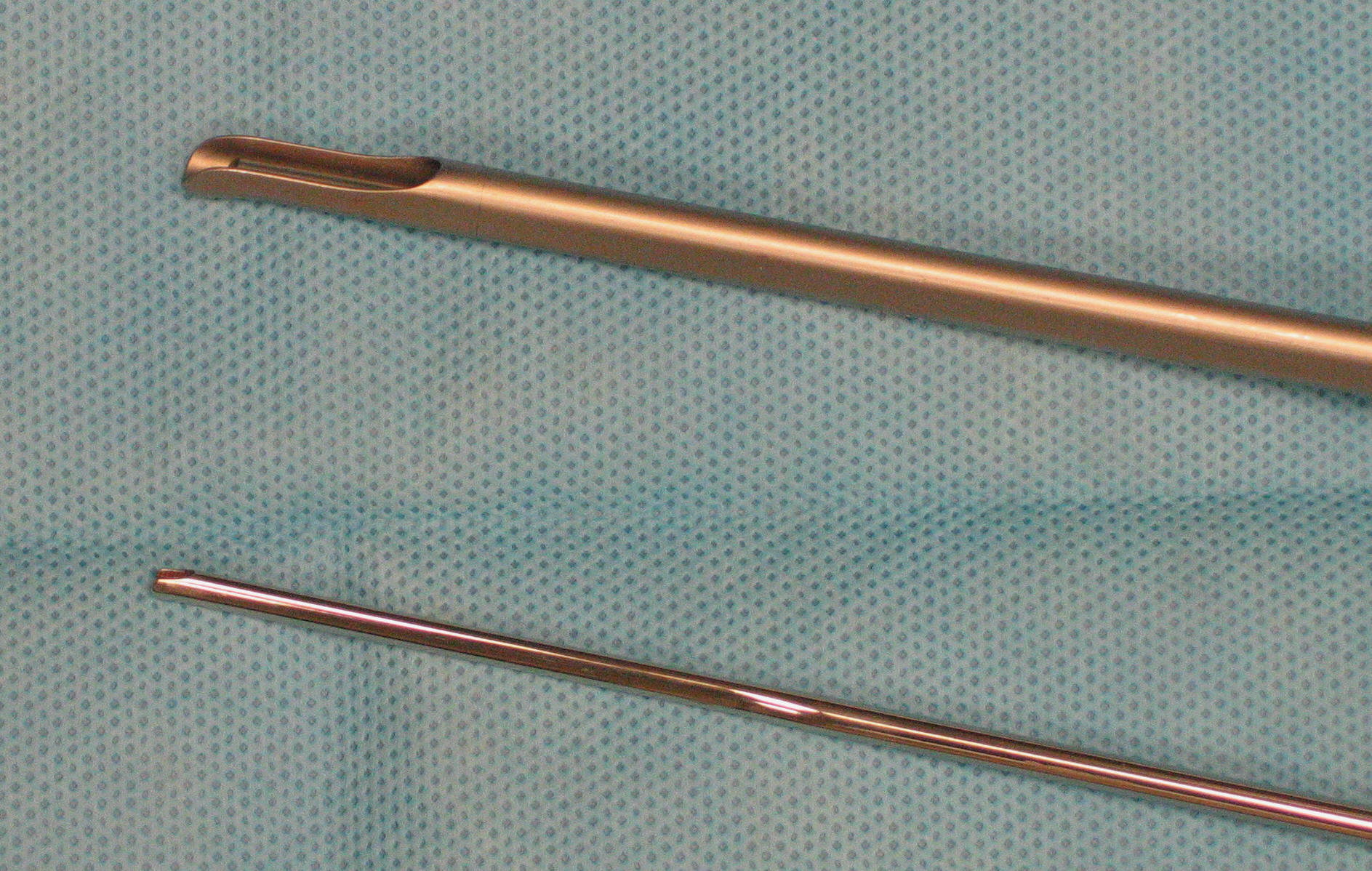

Smaller
diameter
55
cm
scope
on
bottom.
Note
the
smaller
diameter.
The
lens
is
at
the
end
and
the
catheter
channel
enclosed
just
above
the
lens.
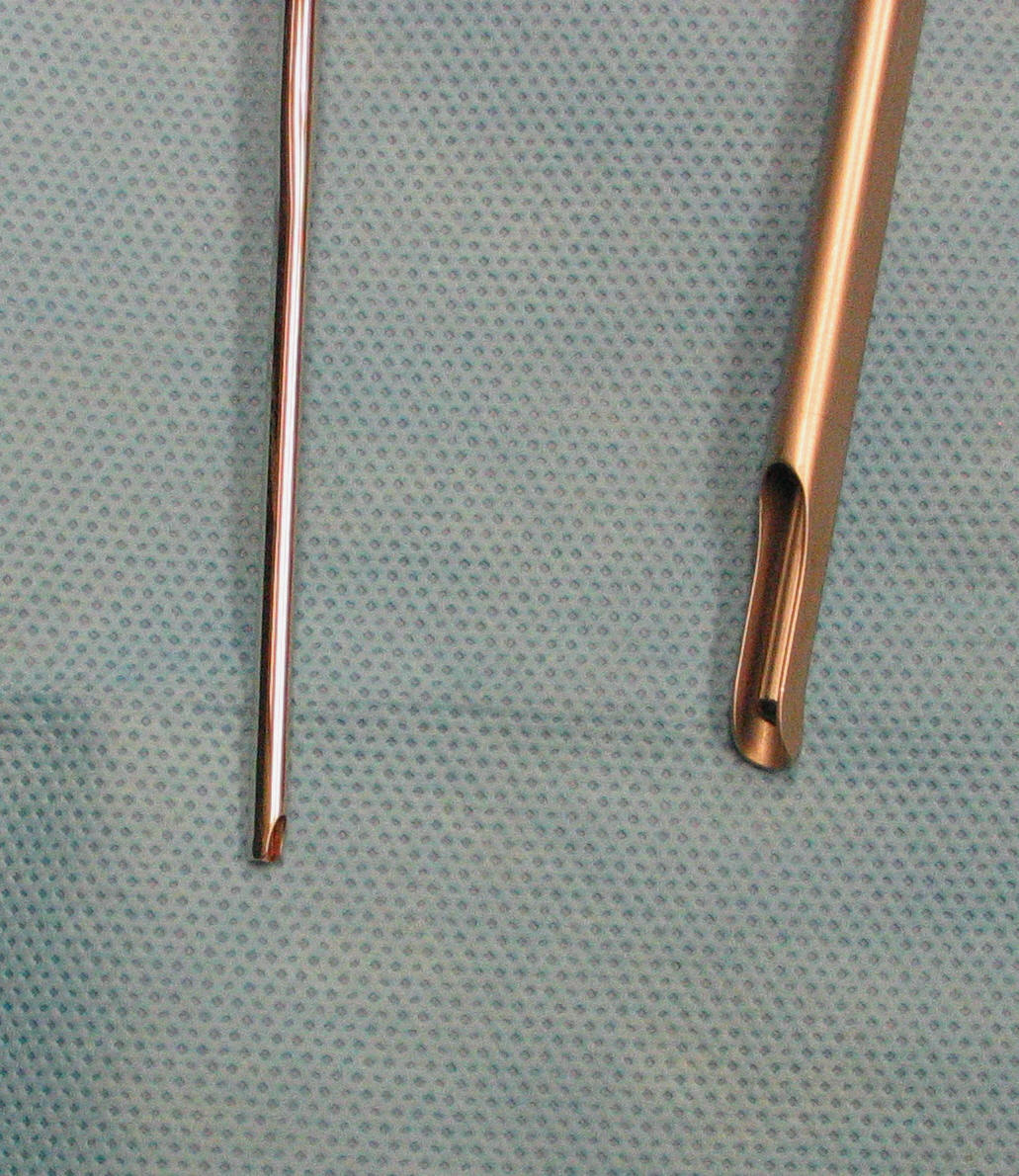 
Smaller
diameter
55
cm
scope
on
left
in
each
picture.
The
lens
is
at
the
tip
and
has
a 60
viewing
angle.
The
lens
at
the
tip
makes
viewing
slightly
more
difficult
because
of
the
collapsing
of
the
vaginal
wall
if
the
catheter
is
not
used
to
hold
the
wall
away.
A
smaller,
longer
catheter
must
be
used.
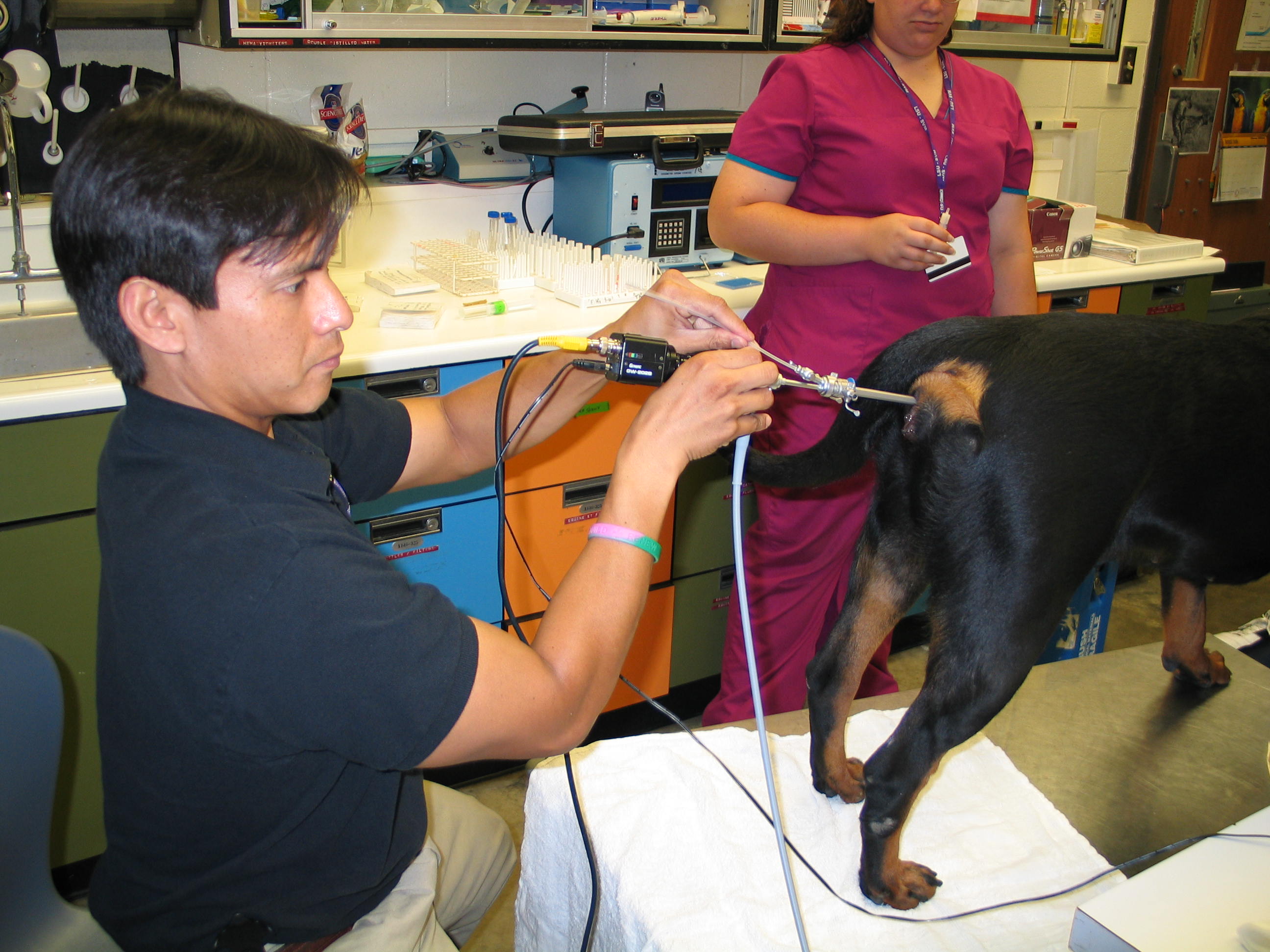
- The cystoscope is passed into the vagina and
the dorsal postcervical fold is identified.
- The cervical os appears as a rosette under the
dorsal post cervical fold.
- An 8 fr catheter is used to inseminate
- Pregnancy rates
- 100% breeding two times using as 200 x 106
cells/breeding
- 85% using as few as 30-50 x 106
cells/breeding
- 57% (the number of breedings and dose
was not stated)

36
cm cystoscope above.
The
lens
is
inset
from
the
end
of
the
sheath
and
the
catheter
channel
is
an
open
channel
in
the
sheath.
- The standard dose for surgical AI is 100-200 million
motile cells in one breeding 5-6 days after the LH peak. Most people
use 100 million cells and breed 6 days after the LH peak or 3 days
after progesterone is 5 ng/ml (15.9 nmoles/ml)
- LSU likes to breed with at least 100 million motile cells on days 5 and 6 post LH.
- Work from South Africa has shown that
fertility can be obtained with as few as 50 million cells deposited
vaginally, every day of estrus.
- The future of frozen semen probably is in multiple
transcervical inseminations of lower doses of semen. This will also
change the way we freeze cells (i.e. we will freeze fewer cells in a
straw.
- At this time all studs that have
semen frozen, need to be DNA tested before registration is allowed.
- To register a litter with the AKC only semen from AKC approved
semen centers can be used. There are a limited number of AKC approved
centers, with LSU being one of them.
- The
AKC only has bookkeeping requirements, they do not endorse any centers
or have any quality control regulations.
- To become approved you must
only show the AKC that you can keep accurate.
Click
here to visit a site of Questions and Answers on Frozen Semen in the
dog.
|


 Canine
Index
Canine
Index Next Page
Next Page