Prolonged
interestrous intervals
- If the interestrus interval is prolonged, it
implies that the pregnancy recognition signal was received, but the
pregnancy was subsequently lost. This results in a heat cycle that
is greater than 21 days long.
- If we make a diagnosis of pregnant followed by
a later diagnosis of non pregnant, this also indicates embryonic
death (assuming our pregnancy diagnosis method is accurate).
- The terms early embryonic death (EED) has been
used for years to indicate that the pregnancy was lost after the
pregnancy recognition signal. As earlier pregnancy diagnostic
methods become available, this will be termed late embryonic death
and EED will be used for embryonic loss before the pregnancy
recognition signal, which would result in a normal 21 day
interestrus interval.
Iatrogenic cause
of Early Embryonic Death
 300 300
- This loss is commonly around 1-7%.
- One study says that palpation of the fetal
membrane slip resulted in more lost pregnancies, however there was a
significant difference among the palpators in the study. This
indicates that the skill of the examiner makes a difference.
- We found no evidence at the University of
Minnesota in the teaching herds investigated there.
- Another study showed that pregnancy rates
decreased, but only minimally, and the cows were checked twice
between 42-46 and 46 days of gestation.
- When the cows are checked makes a difference.
If you examine cows at 30 - 45 days, then you will probably see a
higher embryonic loss. This is because you are getting more of the
ones that would have been lost anyway. If you check at 60 days, all
those that are lost through 60 days are never diagnosed pregnant.
Are you causing the loss????....probably not.
- If palpation is compared to noninvasive methods
of pregnancy diagnoses, the embryonic loss rate is not different.
(Theriogenology 66 (2006)
667.)
- 258 cows pregnant by ultrasound 29-32
days- one FMS - Embryonic loss 14.7%
- 262 cows pregnant by ultrasound only
29-32 days- Embryonic loss 13.47%
- Cows - 16.4% > heifers 8.8%
- We can generally conclude that gentle palpation
does not cause embryonic death.
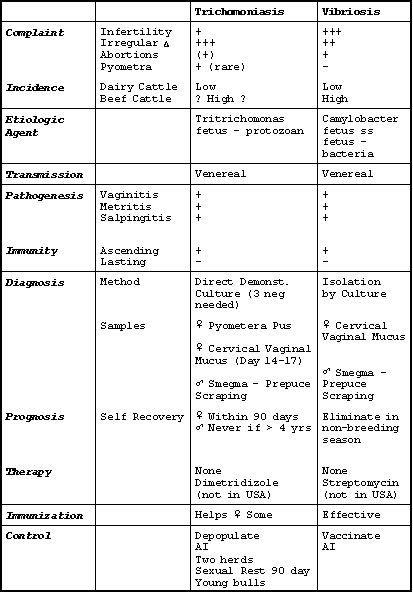
Venereal Diseases
 355-362 355-362
- There are two common venereal diseases in
cattle, Trichomonas fetus (Tritrichomonas
fetus) and Campylobacter
fetus. They cause similar diseases and
may be in a herd together.
Trichomonas fetus (Tritrichomonas fetus)
Clinical signs
- You see a herd infertility, and a prolonged
calving season with a reduced calving rate.
- Post service pyometra or abortion are rare,
postservice pyometra is almost pathognomonic for the disease.
Incidence
- Trich. was isolated in 50% of all cases in
California when Trich. was in the list of rule outs.
Pathogenesis
Female
- When an infected bull contaminates a
susceptible female, Trich. localizes in the vagina, uterus, and
oviduct causing vaginitis and endometritis. You may see some
discharge. At this point there is no
conception failure or interference with the conceptus.
- However, about 50 days post-service the cow has
inflammation of uterus which causes the embryo to die.
- The cow remains infected 2-6 months (some cows
remain infected the duration of pregnancy)
- Eventually the cow gains immunity that lasts
2-6 months (this means that they may be susceptible again next
year).
- The carrier state decreases with time and is
usually eliminated after 2 estrous cycles (is it cycles or time???)
- An infected cow may carry a calf to term and
remain a carrier into next breeding season. This allows herds to
remain infected.
Male
- Males are usually asymptomatic
- The organism localizes in the penile crypts,
prepuce, and anterior urethra. Since the crypts get deeper as the
bull gets older, bulls greater than 4 years old become chronic
carriers, whereas bulls less than 4 years old may have spontaneous
recovery or immunity.
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is by isolation of organisms from the
animal.
Female
- It is commonly found in the pyometra fluid of
postbreeding pyometras. The organism is in the abortion fluids
(amnion, fetal stomach).
- Culturing the cervical vaginal mucus culture
gives poor results. (5/280 in CA study)
Male
- In males the preputial smegma can be cultured.
The sample can be obtained by inserting a dry A.I. pipette into the
preputial fornix and scraping the prepuce while aspirating the
smegma. The sample is transported in special "pouch" or
Lactated Ringers and cultured in Diamond's Media. The media is
examined at 400 power in 24 and 48 hours (examine bottom layer in
tube) to look for organisms. The test is not diagnostic if the
culture is negative, but any positive culture is diagnostic. You
need 3 negative cultures at 1 week intervals to be 90% sure the bull
is free of the organism.

- A PCR
test is available - Transport in
the InPouch TF kit
- The "In Pouch" system for transport
and culture gives improved recovery. (http://biomeddiagnostics.com/tfoetus#info)

Click for information
-
Louisiana Animal Disease
Diagnostic Lab Guidelines
for Tritrichomonas Testing -
click to link to lab site

Treatment
Male
- Dimetridizole works, but is illegal in food
animals in the US. It is given orally for 5 days. The cost is about
$125/bull. It has a bad taste and there may be resistant strains.
- Ipronidazole
- This drug is also illegal for food animals in
the US. To use, give a pretreat of 15,000 I.U./lb. penicillin for 2
days to decrease the Micrococcus organisms that destroy the
imidazole ring.
- It was found to be
100% effective in 30 bulls cultured weekly in
California.
- The cost is about $24/bull.
- Acriflavine (Bovoflavin) is not available in
U.S.. It is applied locally. The treatment is time consuming and no
efficacious. It may however be tried for resistant strains. You can
use the bull after a negative culture 45-60 days post treatment.
Female
- Sexual rest for 2-3 heat cycles will usually
clear the establish resistance.

- Control measures include:
-
depopulation,
-
using A.I.,
-
maintaining an exposed and an unexposed herd (difficult),
-
sexual rest 90 days postpartum with isolation of the unexposed
group,
-
selective culling and use young bulls,
-
cull open cows,
-
test
bulls as a herd survey method, and
-
vaccination .

- The vaccine is a whole cell vaccine made by
Fort Dodge.
 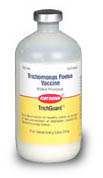
-
Two doses
recommended. One
month and 5 to 7
days before
exposure
-
Compliance is
probably low,
leading to
ineffectiveness
-
It helps clear the infection in weeks (vs
months for natural) and decreases infection rate and increases pregnancy
rate. It appears not to help eliminate the disease in bulls.
Vaccinated cows clear infections sooner. The vaccine is given twice
initially, then an annual booster.
- Comments by veterinarians say it is better
than nothing, but not by much.
Prevention
- Keep a closed herd, so infection cannot be
introduced.
- Test bulls 3 times before entry into the herd.
- Use virgin bulls if possible on clean cows.
- Isolate new females for 90 days (2 heat cycles)
to clear any infection.
Campylobacter fetus
ss. fetus
(Vibriosis)
Clinical signs
- Infertility is seen in 50% of cases. You also
see a delayed return to estrus indicating embryonic death in 50% of
cases.
Pathogenesis
Female
- The semen and the vibrio enter the cervix at
coitus. On the first exposure the organism kills the ova. On the
second exposure the ova survives. About 50% of the ova are destroyed
by 14 days, so the heat cycle is normal.
- The Vibrio is in the cervical mucus 3 weeks to
3 months. Eventually immunity is established after several breedings.
The immunity lasts about 1 year (cows can be reinfected 2-3 years
later).
Male
- Bulls are infected by a carrier cow and the
Vibrio grows in the penile crypts. The is no immunity, but the
infection is eliminated during the non-breeding season. There is no
direct effect on bull fertility, but a bull may become exhausted
from over-breeding, since the cows keep coming back into heat.
Diagnosis
- A tentative diagnosis can be made when you see
repeat breeding cow and a long calving season. Pregnancy rates will
be 20-30% after 60 days of breeding. You may see high pregnancy
rates in heifers bred to virgin bulls and low pregnancy rates in
first calf heifers. This is because the virgin heifers and bulls
have no exposure and the first calf heifers have no immunity when
exposed to the herd breeding situation.
- To confirm a diagnosis a cervical vaginal mucus
culture 3 weeks to 3 months post infection can be taken. Keep the
culture no dry ice if it is longer than 6 hours to get it to a lab.
Culture in Clark's medium. The first positive culture is diagnostic
of herd infection.
- The cervical vaginal mucus agglutinins are of
no value, because false positives are common if the samples are
taken during metestrus.
Bull
- In the bull a preputial wash and culture can be
performed. Again, you need several attempts as false negatives may
occur.

- The virgin heifer test uses a breeding by a
suspect bull to a virgin heifer. You culture the cervical vaginal
mucus 3 weeks post breeding.
Control
- Control measures include A.I. and vaccination.
You should vaccinate cows 30-90 days before breeding, and then
booster annually. Using the vaccine in bulls is experimental only
and may decrease fertility.
Treatment
Male
- Streptomycin is currently unavailable. The dose
was 10 mg/lb subcutaneous for 10 days and ; 5 mg of a 50% solution
locally for 5 days. The animals are susceptible to re-infection.
Female
- Vaccination may hasten recovery.
A summary of Trichomoniasis and
Vibriosis
Hemophilus somnus  367-368 367-368
- Hemophilus is a gm negative nonmotile,
nonsporulating coccobacillus.
-
Normal
vaginal
flora
Clinical signs
- Prolonged interestrous intervals were seen in a
group if cows that cultured positive in the cervical mucus.
- Infertility was seen in a poorly managed dairy
herd. Cervical mucus cultured positive and the bull cultured
positive.
-
Need
pure
culture
and
inflammation
present
to
diaganose
Treatment of cows
and bull and better management
corrected problem.
- Seven months later there were no positive
cultures and fewer problems in the herd. Was it management
primarily??
- Vaccine???
|

