|
LH
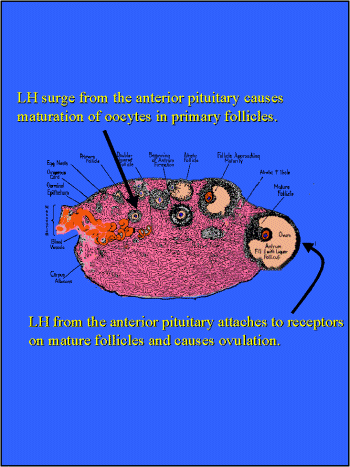 |
- LH is required to stimulate growth of the oocyte
arrested in late prophase of meiosis
in the primary follicles.
- LH attaches to receptors on the mature follicle. It
causes ovulation and luteinization of the follicle about 24-48 hrs
after its release.
- May cause ovulation by causing collagenase release
that breaks down follicle and then stimulates progesterone release
to actually cause ovulation.Glycoproteins (carbohydrate and
protein). This means they are antigenic and will degrade.
- Structure:
2 subunits * Alpha - same within species i.e. LH, FSH, TSH have same
alpha unit within a species. * Beta - same between species i.e. LH
in all species have same beta unit.
- Mechanism of action: *Bind cell membrane and cause
cAMP production, *causes phosphorylation in cell. *a fast action
results.
|
contributed by Bruce
E Eilts on 22-June-2000
modified by Eric Huey
|
