Normal
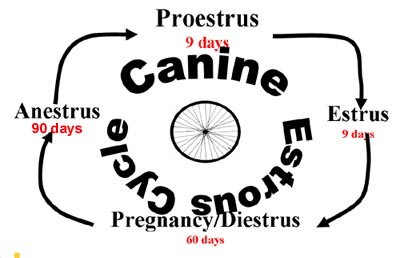
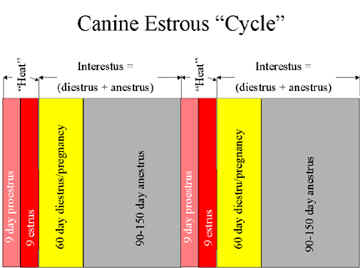
Canine Cycle
- Stages of the cycle are anestrus,
proestrus, estrus, and diestrus.
Anestrus
 p 540-542
p 540-542
 p 28 p 28
- Anestrus is not the same as interestrus.
Anestrus is a variable time after diestrus. Interestrus (diestrus
+ anestrus) averages 5 - 7 months.
- Anestrus lasts 90 - 150 days (anestrus
does not
include diestrus).
- Anestrus is a time of mandatory
endometrial repair that has been documented in Beagles.
Anestrus Endometrial Repair
- The endometrium is being 'repaired' after
the progesterone effects during diestrus for the preceding 60
days.
- True anestrus lasts 90 -150 days post
whelping, or post diestrus.
- Interestrus (anestrus + diestrus) lasts 150 - 210 days after the
last estrus.
- Fertility is low if at least 90 day
anestrus (or a 150 interestrus interval) is not attained. This is
because the uterus has not repaired enough to maintain
pregnancy. (If interestrus is too short, anestrus can be extended using mibolerone or
megestrol acetate, but this will be covered later.)
- The male shows no sexual interest in the
female.
- The female shows no sexual interest in the
male.
- The vulva appears normal. It is not swollen
or edematous.
- The vaginal
cytology has very few cells and
they are noncornified.
- The vaginal wall is very thin and appears
pale on vaginal
speculum examination.
- Progesterone is at baseline concentrations
(<1 ng/ml). Even spayed bitches run basal levels of
progesterone. This baseline progesterone is probably of adrenal
origin.
- Prolactin secretion by the pituitary may
promote anestrus, because prolactin inhibitors can be used to
terminate anestrus (i.e. induce estrus).
Termination of anestrus
(FYI only)
- Increased pulse frequency of LH is seen
late in anestrus.
- FSH is elevated late in anestrus, but
follicles may actually be selected for the next cycle at this
time. This is really not known very well. Inhibin may inhibit
FSH, but it has not been documented in the bitch.
Proestrus

 p527
p527
 p 18 p 18
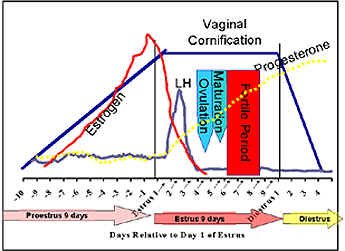
- Proestrus averages 9 days in duration, but
may last from 3-17 days.
- Males are interested in the female.
- Females are not interested in the males.
- The vulva is swollen because of estrogen
secretion by the growing follicles.
- There is serosanguinous discharge from the
vulva that results from diapedesis of RBCs through uterine
vessels.
- The vaginal mucosa appears smooth because
estrogen causes water retention.
- LH has an increased frequency.
- FSH is suppressed.
- Estrogen comes from the growing
follicles and peaks at end of proestrus.
It is actually the decline in estrogen at the end of proestrus
that causes the bitch to show clinical signs of estrus.
- Testosterone is relatively high at the end
of proestrus. This may result from a 'backup' in estrogen
synthesis. This may result in some masculine behavior by the
bitch, such as mounting other dogs.
Proestrus vaginal
cytology
- Parabasal cells
- Superficial cells increase.
Cornification increases approximately 10%/day until
about 100%
of the cells are cornified.
- May or may not see RBCs
- May see a bloody discharge, yet see
no RBC's on the vaginal smear.
- WBC, mostly PMNs may be present.
Proestrus vaginoscopy
- The mucosa is glistening.
- There are rounded edges to mucosa
because of the water retention in the cells.
Estrus

 p 534
p 534
 p 22 p 22
Estrus 'events'
- Estrus averages 9 days in duration,
but can be as short as 3 days or as long as 21 days.
- The male and female are both
interested in each other.
- The bitch will 'flag' her tail, as if
allowing access to the vulva.

Click to see 'Flagging'
- The estrous behavior results from the
estrogen that peaked during proestrus abruptly declining.
If this decline is prevented (i.e. giving exogenous
estrogen), then the bitch will not show signs of estrus.
Estrus
Vaginal
cytology
- The smear is very cellular. Many more
cells than in anestrus.
- Greater than 90% of the cells are
cornified. Most of the cells are usually anuclear cells.
- The PMN's are gone because the
hyperplastic vaginal wall is too thick for them to cross
the mucosa.
- RBC's are generally gone.
- The background of the smear becomes
very clean.
- The cells may slough off on sheets as
the end of estrus approaches.
- The vulva and vaginal epithelium appear to
wrinkle because the decreased estrogen results in water loss of
the cells.
Ovulation

- LH peaks about 24-48 hours into
estrus and is caused by the estrogen peak during proestrus.
The LH surge causes ovulation of the ovarian follicles.
- LH has a very short peak duration and
must be assayed every day in order to detect the peak
rise.
An in-house test is available to detect the LH peak, but
you must test daily to identify the surge.
- Ovulation occurs 24-48 hours after LH
surge (day 3-4 of estrus)
- Ovulation takes about takes 24 hours
for all oocytes to be ovulated. A '2N' oocyte is ovulated
and the oocyte must undergo reduction division, which
takes 2-3 days, before the oocyte is ready for
fertilization. During this time the polar
body extruded (a 1N 'nuclei'
of chromosome).
- If it is not fertilized, the oocytes die
3-4 days post maturation (5-6 days post ovulation).
- The fertile period of breeding is
generally recommended as the 3rd to the 5th days of
estrus, or every other day of estrus.
- Ultrasound is poor at determining
ovulation because the follicles do not appear to luteinize,
they remain anechoic.
Progesterone during estrus

- Progesterone starts to rise during
estrus. The initial rise usually coincides with the LH
peak.
- The preovulatory rise in progesterone
is caused by estrual luteinization of follicles and a
'backup' in progesterone from the estrogen synthesis.
- The progesterone rise that coincides
with the LH rise can be measured with an ELISA kit and be
used to time fertile period.
- Since progesterone starts to rise
coincidentally with the LH peak, when estrus ends the
progesterone is already greatly elevated over baseline.
Androstenedione
 Click to see a PowerPoint of the Canine Estrous Cycle and Ovulation
Diestrus

 p 539
p 539
 p27 p27
- Diestrus is the time of progesterone
dominance. The hormonal events of diestrus can be, for
learning sake, identical in pregnant and non-pregnant
bitches
- This is not really true.
- Progesterone is lower overall in
non-pregnant bitches
- Prolactin is lower in bitches
that do not show overt pseudopregnancy.
- Diestrus in the non-pregnant bitch could be called covert
pseudopregnancy, since progesterone remains elevated, but
there are no signs of pregnancy.
Diestrus 'events'
- The bitch refuses male's advances.
This refusal is quite variable in when it occurs.
- The duration of diestrus is about 60
days, whether or not the bitch is bred and/or pregnant.
Diestrus vaginal
cytology
- There is an abrupt change from
the 100% to less than 50% cornification on the first
day of diestrus.
- The PMN's return to clean up all
the sloughed cells and debris.
- Intermediate cells return as well
as 'metestrum' cells and foam cells.
Diestrus progesterone
- Progesterone comes from the corpora
luteal
- Promotes endometrial glands
development.
- Promotes mammary alveolar glands.
- Antagonizes estrogen.
- Progesterone rises throughout
diestrus.
- Progesterone peaks at 15-30 days of
diestrus at 15-80 ng/ml.
- Progesterone is overall lower in
nonpregnant bitches, but there is too much overlap to use
lower progesterone concentration as a pregnancy test.
- Progesterone declines to less than 1
ng/ml 60-100 days after the first day of diestrus.
- Progesterone production is dependent
upon LH and prolactin production by anterior pituitary.
Prolactin in diestrus
- Luteotropic
- It is higher in pregnant bitches than in non-pregnant
bitches.
- Rises with fall of progesterone in
pregnant bitches
- Higher in overtly pseudopregnant bitches than non-pregnant bitches without
overt pseudopregnancy.
- Causes mammary development.
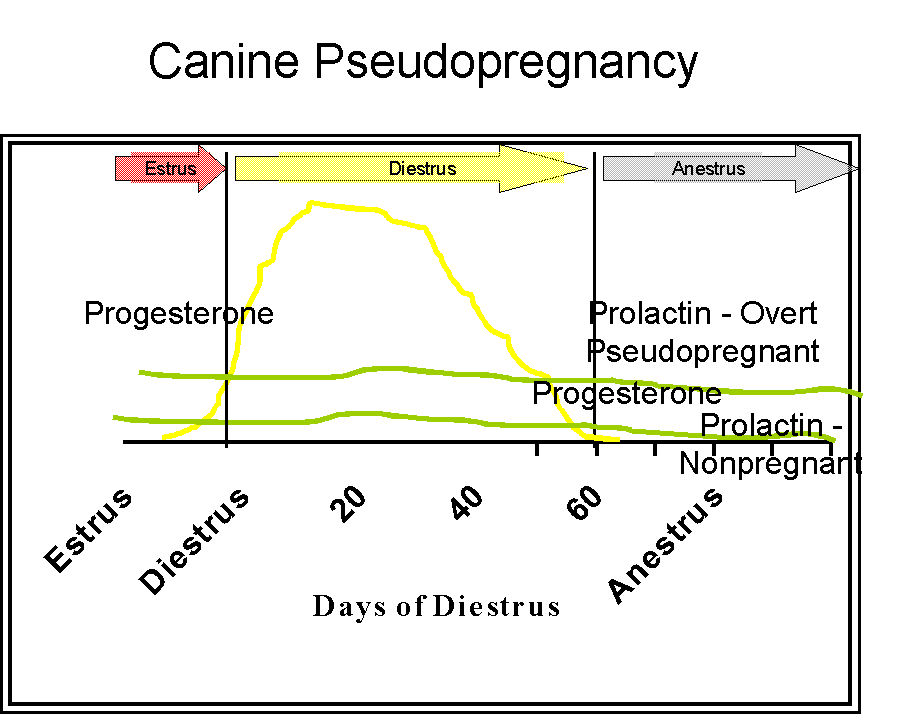
Cessation of diestrus
- No known luteolytic PGF secreted from
the uterus in non-pregnant bitches.
- Hysterectomy has no
effect on the luteal lifespan.
- Prostaglandins are luteolytic in the
bitch as early as 5 days after the beginning of diestrus.
The dose is usually cited as 0.1 - 0.25 mg/kg SID-TID for
3-5 days, but progesterone must be followed to ensure
luteolysis.
|
Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
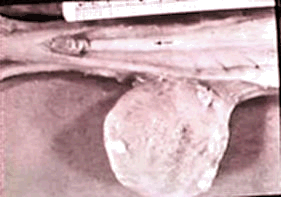
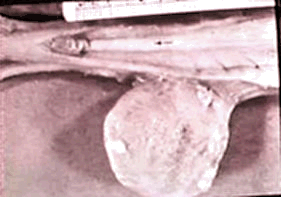
Below - A sagital section of the canine vagina
during proestrus.
The
arrow is on the dorsal median
postcervical fold and pointing toward
the cervix.
Click
to enlarge

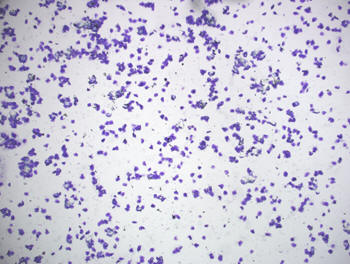
Below -A fully cornifed estrual smear with a clear
background.
Click here to see a PowerPoint
Auto tutorial on
Canine Vaginal Cytology
Below -The wrinkled vaginal mucosa seen at the
beginning of estrus.
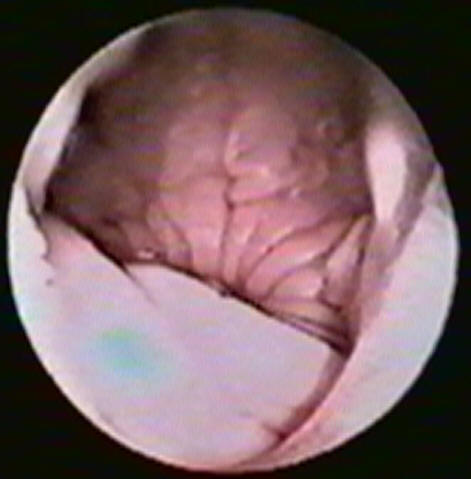
As viewed through a vaginoscope.
Below -
Dr. Richard Fayrer-Hosken from the
University of Georgia
showing the
'wrinkled' vulva at estrus.
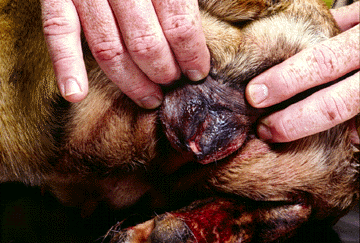
Click to enlarge

Click to enlarge
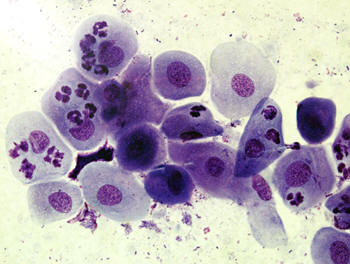
Abrupt change to diestrus cytology.
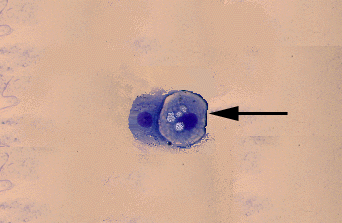
Below -Foam cell. I have seen these, but rarely
during diestrus. Eilts.
Photo from U of Georgia, Dr. Fayer-Hosken
Click to enlarge

|

 Next Page
Next Page